Angular Reacitve Form 內有一套值的更新流程,從 FormGroup 到 FormControl 間到底是如何進行資料的更新,有什麼要留意的地方,在這篇筆記內我盡量整理 (會持續潤稿)
首先先將重點放在 FormGroup 和 FormControl 這兩個主體上就好,我們都知道 FormGroup 和 FormControl 都是繼承 AbstractControl,不同的部分就在各 class 上重新撰寫 ,好加在的是這篇文章要看的程是碼都在同一個檔案上
而此篇要探討的是 setValue、patchValue 和 valuechanges 這三件事情,到底更新的流程是什麼,為什麼這件事情很重要,當在寫連動表單或是物件時,流程一但搞錯就會讓你除錯除到死
原始碼解析
先從最底層的元件來看,對於 FormControl 來說,patchValue 與 setValue 是沒有差異的,即使呼叫 patchValue,還是會去執行 setValue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| patchValue(value: any, options: {
onlySelf?: boolean,
emitEvent?: boolean,
emitModelToViewChange?: boolean,
emitViewToModelChange?: boolean
} = {}): void {
this.setValue(value, options);
}
|
而 setValue 會執行的程是碼其實也不多,所有的工作都落在 updateValueAndValidity 上
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| setValue(value: any, options: {
onlySelf?: boolean,
emitEvent?: boolean,
emitModelToViewChange?: boolean,
emitViewToModelChange?: boolean
} = {}): void {
(this as {value: any}).value = this._pendingValue = value;
if (this._onChange.length && options.emitModelToViewChange !== false) {
this._onChange.forEach(
(changeFn) => changeFn(this.value, options.emitViewToModelChange !== false));
}
this.updateValueAndValidity(options);
}
|
updateValueAndValidity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| updateValueAndValidity(opts: {onlySelf?: boolean, emitEvent?: boolean} = {}): void {
this._setInitialStatus();
this._updateValue();
if (this.enabled) {
this._cancelExistingSubscription();
(this as {errors: ValidationErrors | null}).errors = this._runValidator();
(this as {status: string}).status = this._calculateStatus();
if (this.status === VALID || this.status === PENDING) {
this._runAsyncValidator(opts.emitEvent);
}
}
if (opts.emitEvent !== false) {
(this.valueChanges as EventEmitter<any>).emit(this.value);
(this.statusChanges as EventEmitter<string>).emit(this.status);
}
if (this._parent && !opts.onlySelf) {
this._parent.updateValueAndValidity(opts);
}
}
|
主要程式碼是寫在 AbstractControl 裡
-
line 2: 取得目前物件的狀態,如果是 disabled 的話,則 status 將會是 DISABLED 不然就是 VALID
-
line 3: 只有在 FormGroup 和 FormArray 有實做,根據目前 Group / Array 內子物件的值更新本身的值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
_updateValue(): void {
(this as {value: any}).value = this._reduceValue();
}
_reduceValue() {
return this._reduceChildren(
{}, (acc: {[k: string]: AbstractControl}, control: AbstractControl, name: string) => {
if (control.enabled || this.disabled) {
acc[name] = control.value;
}
return acc;
});
}
|
-
line 5 ~ 13: 如果物件狀態是 enabled 才會進行驗證動作,驗證的順序為
- 同步驗證先執行,並更新狀態
- 如果狀態是
VALID 或是 PENDING 才會進行非同步驗證
-
根據傳入參數 emitEvent 來決定是否觸發 valueChanges 和 statusChanges
-
根據 onlySelf 來決定是否要觸發父層的 updateValueAndValidity
這裡有一個小技巧,所傳入的參數值並沒有設定預設值,而是很明確指定判斷值,這招可以學一下
1
2
3
| if (opts.emitEvent !== false) {
...
}
|
patchValue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| patchValue(value: {[key: string]: any}, options: {onlySelf?: boolean, emitEvent?: boolean} = {}):
void {
Object.keys(value).forEach(name => {
if (this.controls[name]) {
this.controls[name].patchValue(value[name], {onlySelf: true, emitEvent: options.emitEvent});
}
});
this.updateValueAndValidity(options);
}
|
- 會先更新子物件,並設定只會更新子物件本身
- 在跑自己的
updateValueAndValidity
細節
一般使用基本上不會遇到什麼問題,但如果遇到連動的情況,就要特別小心
1
2
3
4
| formData = new FormGroup({
firstName: new FormControl(),
lastName: new FormControl()
});
|
情境 1
請各位想想根據第一段的原始碼解析,這邊跑出來結果會是什麼呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| this.formData.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("formGroup", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.firstName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("firstName:", value, "formGroup value:" ,this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.lastName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("lastName:", value, "formGroup value:" ,this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.patchValue({
firstName: "1",
lastName: "2"
});
|
結果如下
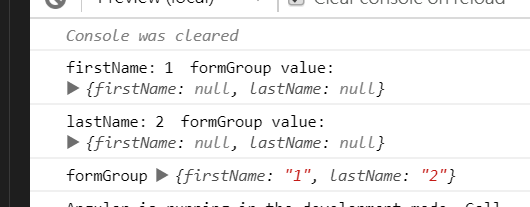
為什麼呢? 來模擬一下執行的步驟
formGroup.patchValue : 會根據傳進去的資料依序更新 firstname 與 lastName formControlfirstName FormControl 更新自身的值,但因為 FormGroup 傳入 onlySelf 為 true,所以不會更新 parent 的值lastName FormControl 更新自身的值,但因為 FormGroup 傳入 onlySelf 為 true,所以不會更新 parent 的值FormGroup 執行 updateValueAndValidity- 根據
children 更新自身的值
- 送出
valueChanges event
- 結束
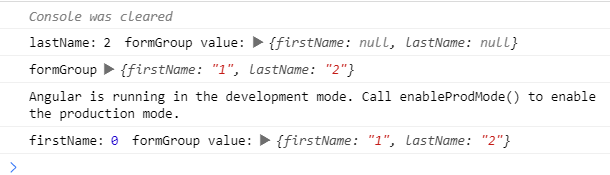
情境 2
這邊跑出來結果會是什麼呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| this.formData.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("formGroup", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.firstName.valueChanges
.pipe(tap(() => this.formData.controls.lastName.setValue("3")))
.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log(
"firstName:",
value,
"formGroup value:",
this.formData.value
)
});
this.formData.controls.lastName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log("lastName:", value, "formGroup value:", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.patchValue({
firstName: "1",
lastName: "2"
});
|
結果如下
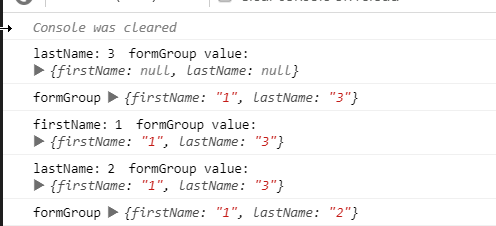
你想對了嗎? 我們來模擬一下執行的步驟
formGroup.patchValue : 會根據傳進去的資料依序更新 firstname 與 lastName formControlfirstName FormControl 更新自身的值,但因為 FormGroup 傳入 onlySelf 為 true ,所以不會更新 parent 的值- 過程中去執行更新
lastName FormControl 的值 ,參數接為預設值,所以 emitEvent: true,onlySelf:false
- 觸發
lastName FormControl 的 valueChanges
- 觸發父層的
updateValueAndValidity
firstName FormControl 自身 valueChanges 流程跑玩lastName FormControl 更新自身的值,但因為 FormGroup 傳入 onlySelf 為 true,所以不會更新父層的值FormGroup 執行 updateValueAndValidity- 根據
children 更新自身的值
- 送出
valueChanges event
- 結束
情境 3
這邊跑出來結果會是什麼呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| this.formData.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("formGroup", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.firstName.valueChanges
.pipe(tap(() => this.formData.controls.lastName.setValue("3", {emitEvent: false})))
.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log(
"firstName:",
value,
"formGroup value:",
this.formData.value
)
});
this.formData.controls.lastName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log("lastName:", value, "formGroup value:", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.patchValue({
firstName: "1",
lastName: "2"
});
|
結果如下,你想對了嗎?
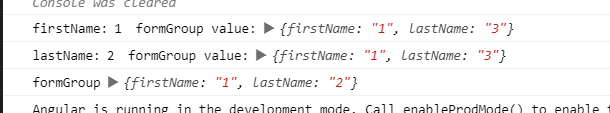
情境 4
這邊跑出來結果會是什麼呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| this.formData.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("formGroup", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.firstName.valueChanges
.pipe(tap(() => this.formData.controls.lastName.setValue("3", {emitEvent: false, onlySelf: true})))
.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log(
"firstName:",
value,
"formGroup value:",
this.formData.value
)
});
this.formData.controls.lastName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log("lastName:", value, "formGroup value:", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.patchValue({
firstName: "1",
lastName: "2"
});
|
結果如下,你想對了嗎?
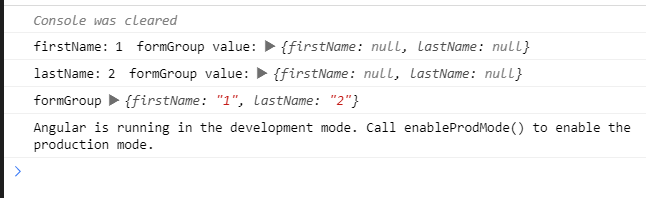
情境 5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| this.formData.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value => console.log("formGroup", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.controls.firstName.valueChanges
.pipe(
mergeMap(() =>
timer(1000, 0).pipe(
take(1),
tap(() =>
this.formData.controls.lastName.setValue("3", {
emitEvent: false,
onlySelf: true
})))
)
)
.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log(
"firstName:",
value,
"formGroup value:",
this.formData.value
)
});
this.formData.controls.lastName.valueChanges.subscribe({
next: value =>
console.log("lastName:", value, "formGroup value:", this.formData.value)
});
this.formData.patchValue({
firstName: "1",
lastName: "2"
});
|
結果如下,你想對了嗎?
心得
Reactive Form 將 valueChanges 包成 Observable 是很方便,要做一些連動的動作可以如流水般的操作,但問題是,如果資料流的線路沒搞對,就會發生為什麼這裡取的資料是錯的問題發生。這些細節的部分都是文件中沒有提到的
所以,在 FormControl 的 valuechanges 流中操作其它 FormControl 的值要特別小心,務必確認同步與非同步的發生順序




